At the same time, companies in most sectors today understand that treating sustainability only as a compliance issue is no longer an option. A poorly defined, poorly implemented sustainability strategy has significant negative consequences. Details about some of these are here.In Consumer products and retailing: How sustainability is fundamentally changing consumer preferencesCapgemini Research Institute found that 79 percent of consumers change purchase choices based on consistency—and that consistency has the potential to significantly impact customer experience, happiness and loyalty.
- Companies in certain sectors such as automotive, consumer goods and retail, and energy are particularly vulnerable to the impact of sustainability on brand image. But sustainability issues have the potential to affect any organization. For example, just as sustainability strategies inform consumers’ purchasing decisions, they influence a company’s reputation with its B2B customers and its desirability as a place to hire.
- Investors are increasingly evaluating net-zero strategies before investing in a company. A poorly defined strategy makes it difficult for companies to attract this important source of funding, and incomplete, inaccurate or unreliable data is a barrier to proving the strategy’s effectiveness.
- Climate change and extreme weather events are already having a massive impact on companies across all industry sectors. Without a solid sustainability strategy, it is difficult for organizations to assess risk and take steps to avoid such events or mitigate their consequences.
These few examples make it clear that sustainability performance and financial performance are intrinsically linked – which is why many companies now assign responsibility for environmental performance to the chief financial officer.
Measurement and innovation
In today’s data-driven business environment, having high-quality data is essential for an organization to comply with regulations and benefit from a strong sustainability strategy. But few organizations have the tools, technologies, processes, and culture needed to capture, qualify, and process reliable data. Collecting and managing high-quality sustainability data should be every company’s first objective.
The good news is that once this is achieved the company can start to innovate that data. AI is a powerful tool for this, as it can integrate data from across the enterprise – as well as from upstream and downstream sources such as suppliers, distributors and retailers – and then derive insights, make recommendations and business operations and share them. value chain. A few examples from my work at Capgemini Insight:
- Developing an AI-powered simulator to anticipate and mitigate the carbon impact of proposed IT projects for a company in the mining industry
- Using AI to review production operations at another company in the mining industry to reduce the carbon footprint of its raw materials use
- Using AI to assess consumer shopping behavior, reducing fresh fruit waste for a European retailer
- Implementing AI-optimized processes can help a manufacturer reduce energy consumption and costs by seven percent.
Anticipation and Digital Twins
Companies can use the data to anticipate the impacts of sustainability decisions on company performance. For example, subcontractors with excellent sustainability records are usually not the cheapest option, so companies must decide how to balance financial performance with sustainability performance – and then convince stakeholders such as investors that this is the right decision.
In such cases digital twins emerge as a useful tool. Digital twins allow companies to use their data to create a virtual representation of their operations, then apply simulations to the data using AI and other technologies and measure outcomes. Changes can have significant, organization-wide effects, both positive and negative, affecting everything from customer satisfaction to financial performance. It is important that decision makers have the opportunity to test and evaluate such ideas before implementing them.
As with many new initiatives, companies hoping for success must take a pragmatic approach. Articulate a clear vision and focus on internal assets before incorporating data from partners, subcontractors, customers and other external sources. AI-derived insights can help decision makers prioritize sustainability issues. Companies can focus on a pilot project before expanding the company’s ecosystem.
Data mastery connects sustainability with innovation
Companies that become data masters can easily provide the information they need to comply with environmental regulations. But that’s just the beginning. Whether it’s helping R&D develop new products and services, providing marketing with insights to boost brand image, or identifying new business models the company can consider, data masters can use AI tools and that strong data foundation to help drive innovation. across the organization’s ecosystem, and accelerates the organization’s sustainable transformation.
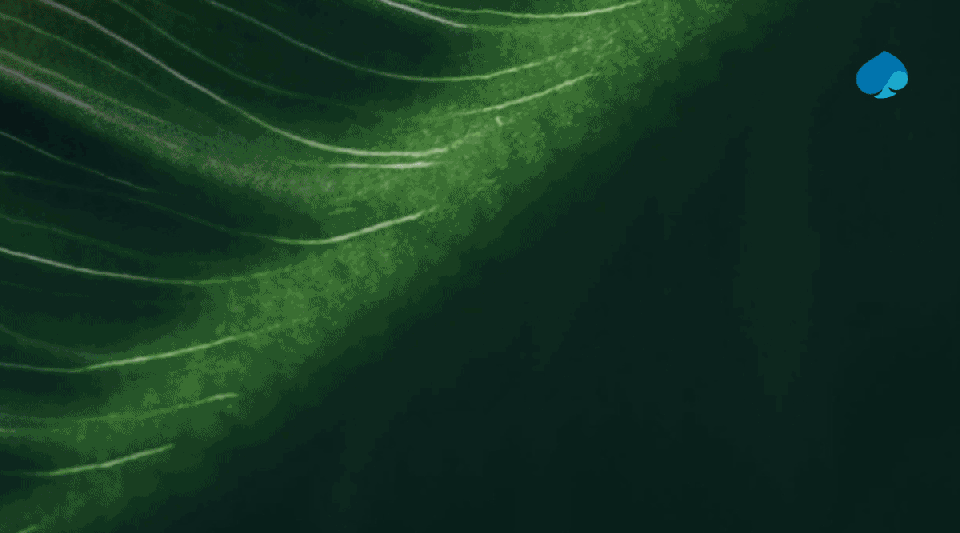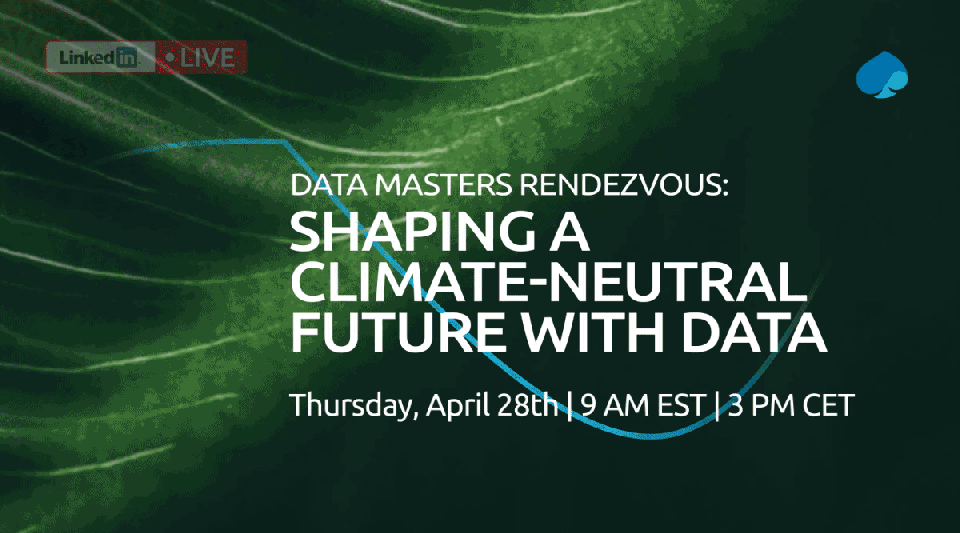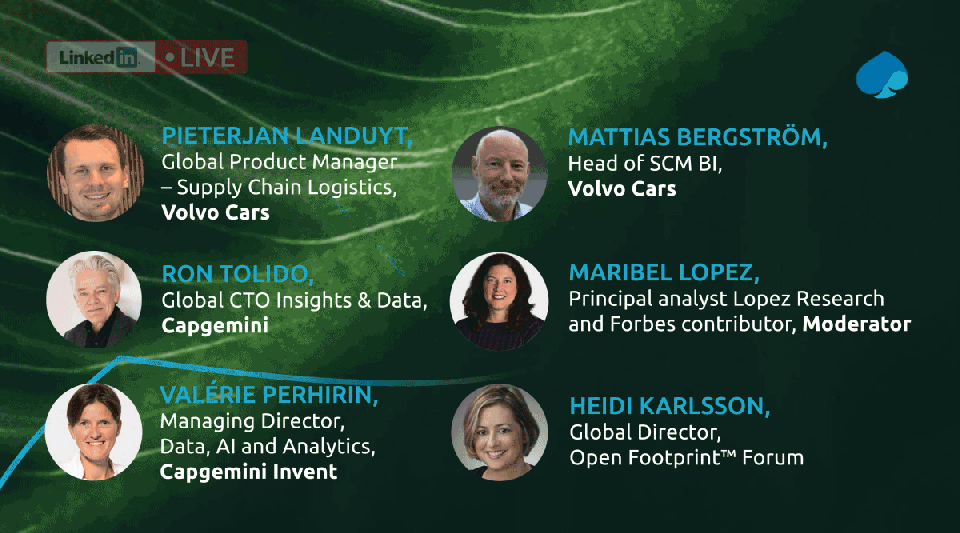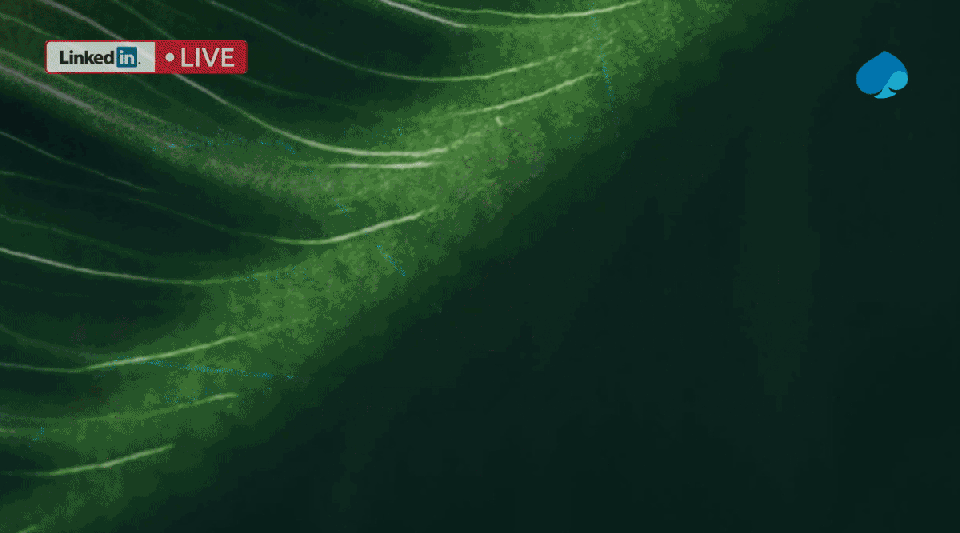
Watch our Linkedin Live where we discuss how companies like Volvo Cars go to net-zero:
Findings
Sustainability is more than compliance
Accurate, reliable stability data is essential to satisfy regulatory compliance. But many people – from consumers to investors – are also demanding high-quality data about a company’s sustainability strategy.
AI powers sustainable innovation
Applying AI to high-quality sustainability data is an opportunity to innovate in ways that build brand image, attract investment, lower operating costs and reduce risk.
Find availability
Companies must walk a fine line between sustainable performance and financial performance. AI-powered simulations can help companies stay on the right track while avoiding missteps.
Interesting to read?
Capgemini’s innovation launch, Data Driven Innovation Review | Wave 4 consists of 18 articles authored by leading Capgemini and partner experts – from digital twins in the industrial metaverse to „slave” AI, serendipity in user experiences, permacomputing and the fight against data waste. .. In addition, there are major technical partners in cooperation, such as several articles Alation, Cognition, Toucan Togo, Data RobotAnd Open group To rethink what is possible.

