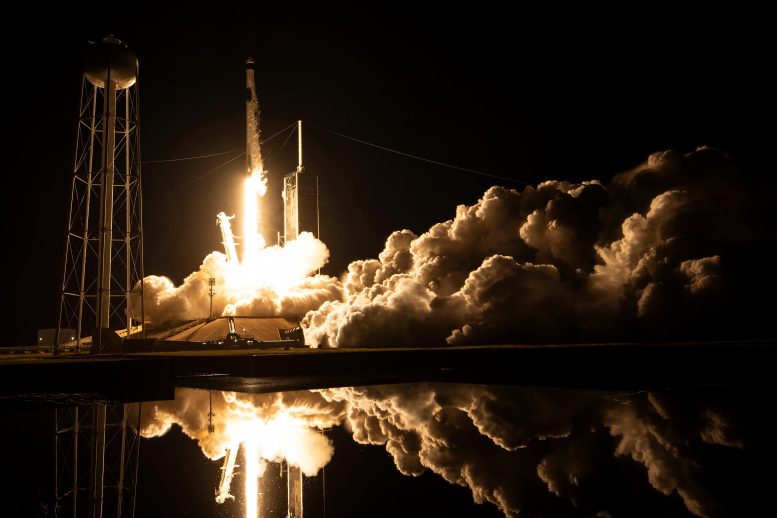

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon spacecraft was launched from Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Nov. 9, 2023, to the International Space Station for the company's 29th commercial resupply mission. Liftoff is at 8:28pm EST. Credit: SpaceX
NASA And the agency's international partners send scientific investigations International Space Station On the 30th SpaceX Commercial redistribution services work, including trials of technologies such as monitoring sea ice, automating 3D mapping, and developing nanoparticle solar cells. The company's Dragon cargo shuttle is scheduled to lift off from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 4:55 p.m. EDT on Thursday, March 21.
Read more about some of the research traveling to the orbiting lab:
Extraterrestrial plants
Plants can be used in regenerative life support systems, provide food, and contribute to the well-being of astronauts on future deep space exploration missions. C4 photosynthesis in space (APEX-09) investigates how microgravity affects the mechanisms by which two species of grasses, C3 and C4, capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
„Plants respond to stress situations based on their genetic makeup and environment,” said Bubutu Handakumbura, principal investigator at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. „We aim to uncover the molecular changes in plants exposed to spaceflight stresses and develop an understanding of the mechanisms involved. Photosynthesis in space.” The results may elucidate plant responses to stressful environments and inform future work on the design of bio-regeneration support systems and systems for plant growth on Earth.
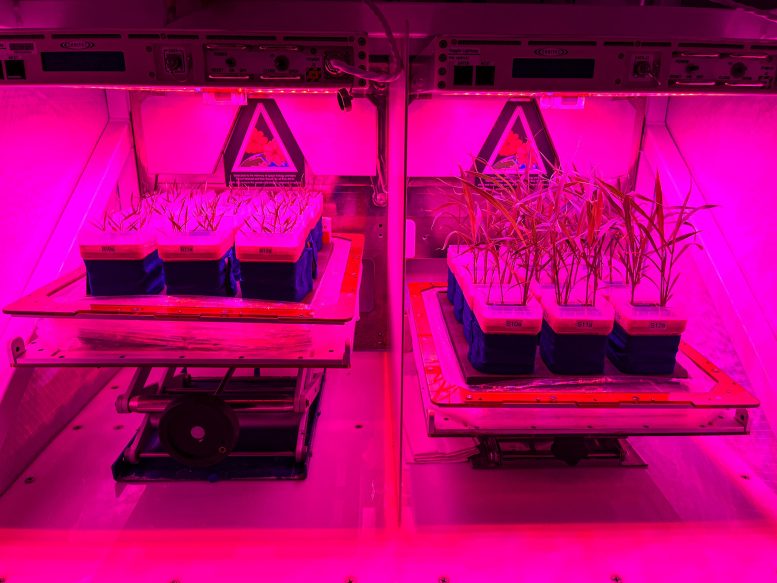

Brachypodium and Cetaria were grown in plant growth systems (PGS) and tested under International Space Station environmental conditions using Veggie units at NASA's Kennedy Space Center during the APEX-09 experimental validation experiment. Thanks: Bubutu Handakumpura
Sensing the ocean
The ocean significantly influences global climate. A technique called Global Navigation Satellite System Reflectometry (GNSS-R), which receives satellite signals reflected from Earth's surface, shows promise as a way to monitor ocean phenomena and improve climate models. KILLIC-1: A GNSS Reflectometry Cubesat to Measure Sea Ice Thickness and Extent (Nanorocks Killick-1) experiments using this technique to measure sea ice. The program supports the development of space and science capabilities in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada by providing space systems and Earth observation experience. More than 100 undergraduate and postgraduate engineering students participated in it.
„The most exciting aspect of this program is that students have the opportunity to embark on a mission in space,” said Desmond Power, co-investigator with Canada's C-CORE. „It's exciting to build a small satellite that does a lot of different things, including contributing to our knowledge of climate change.”
GNSS-R technology is low cost, light and energy efficient. Its potential applications on Earth include providing data for weather and climate models and improving understanding of ocean phenomena such as surface winds and storm surges.
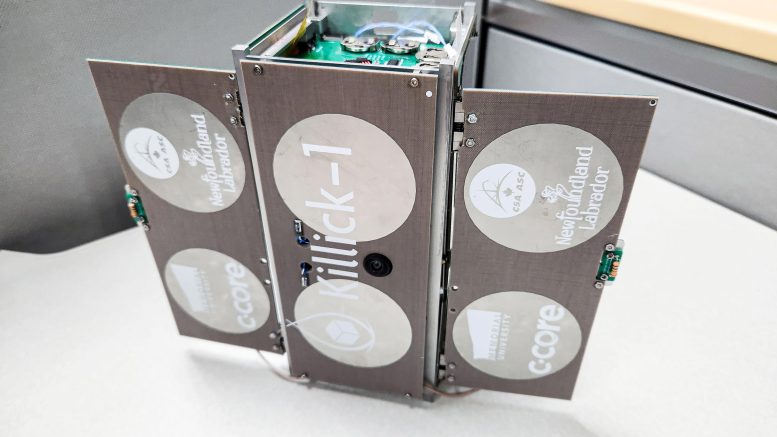
A fully assembled NANOROX-GILLIC-1 cubesat with its Global Navigation Satellite System Reflectometry (GNSS-R) antenna. Measuring sea ice using Nanoracks-Killick-1 GNSS-R. Potential applications of GNSS-R include providing data for weather and climate models and improving understanding of ocean phenomena such as surface winds and storm surge. Credit: C-Core and Memorial University.
Automatic autonomous assistance
The Multi-Resolution Scanner (MRS) payload for Astrobee (Multi-resolution scanning) testing technology for automating 3D sensing, mapping, and situational awareness systems.
„Our MRS aboard the Astrophy free-flying robot will create 3D maps of the interior of the space station,” said Mark Elmouti, project leader with Australia's National Science Institute. CSIRO, which developed the technology in collaboration with Boeing. “The scanner integrates technologies developed by our mining and robotics teams. By combining data from multiple sensors, we compensate for weaknesses in any one system. It provides very high-resolution 3D data and very precise trajectory data to understand how the robot is moving in space.”
„The technology is used to operate spacecraft autonomously with little or no human intervention, where robots must sense the environment and maneuver precisely, including the Lunar Gateway space station,” said Connie Miller, Boeing's principal investigator. „Other applications may include the inspection and maintenance of spacecraft and autonomous vehicle operations on other celestial bodies. The results support improvements in robotic technologies for harsh and dangerous environments on Earth.
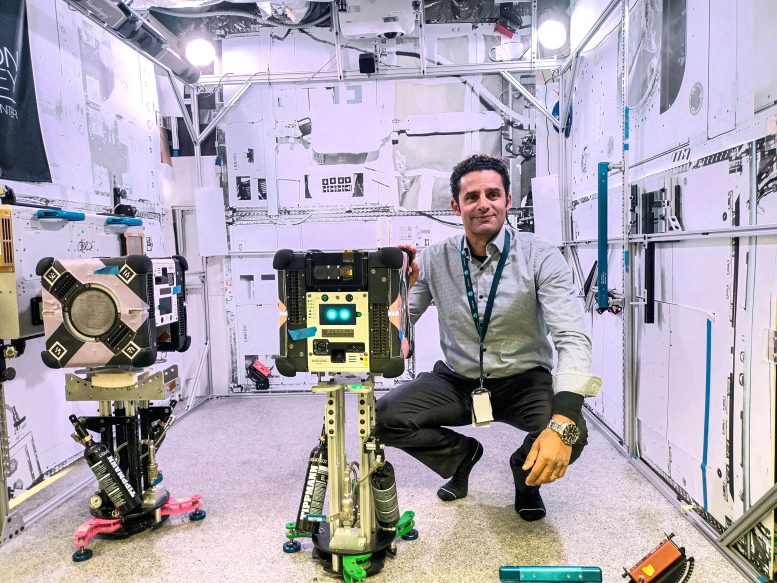

CSIRO project lead Mark Elmouty prepares for final pre-flight testing with the MRS hardware and Astrobee robot. Credit: NASA
Location of particles
The Nanoparticle halo suspension The study examines how nanoparticles and microparticles interact in an electric field. Principal Investigator Stuart J. of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Louisville. According to Williams, a process called nanoparticle haloing uses charged nanoparticles to enable precise particle arrangements that improve the performance of quantum-dot integrated solar cells.
Quantum dots are tiny spheres of semiconductor material capable of converting sunlight into energy. Conducting these processes in microgravity provides insight into the relationship between shape, charge, concentration and interaction of particles.
The investigation is supported by NASA's Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR), which partners with government, higher education, and industry on research infrastructure and programs to improve research and development capacity and competitiveness.
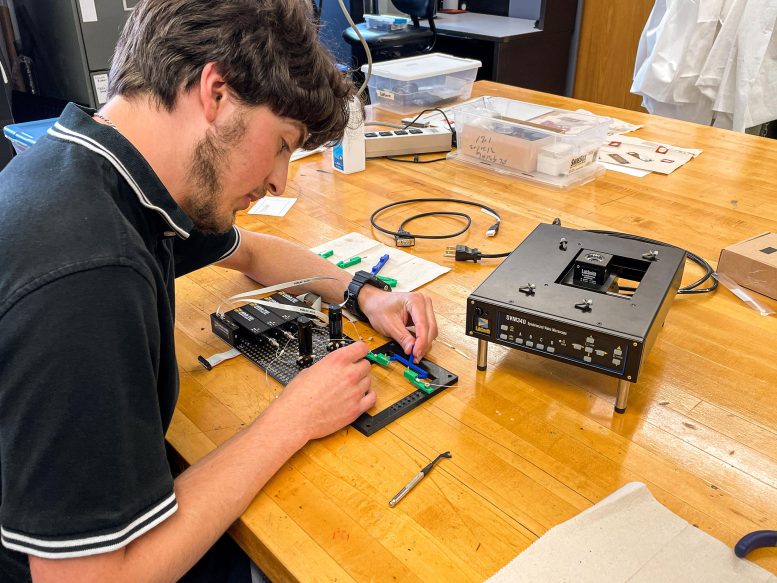

A capstone student assembles a microscope and liquid breadboard for a nanoparticle haloing suspension payload. This payload tests the controlled assembly of nanoparticles in zirconia and titanium-dioxide-coated silica solution. A useful demonstration could lead to applications in an improved solar cell manufacturing technology called quantum-dot solar synthesis. Credit: University of Louisville

„Oddany rozwiązywacz problemów. Przyjazny hipsterom praktykant bekonu. Miłośnik kawy. Nieuleczalny introwertyk. Student.
